Infection by genital HPV human papillomavirus is very common in those who are sexually active. Whether symptoms occur or not can depend on the type of HPV virus involved- in some HPV infections genital warts are seen, while in some, the symptoms are not entirely visible. Some are associated with cervical and other types of cancer, in which no warts are seen but some other HPV types cause common warts on hands or feet. Most people who are infected by genital HPV will clear it without treatment and no health problems occur. The longer the virus is in the body, however, the higher is the risk of developing health problems such as cervical or anal cancer.
HPV Symptoms
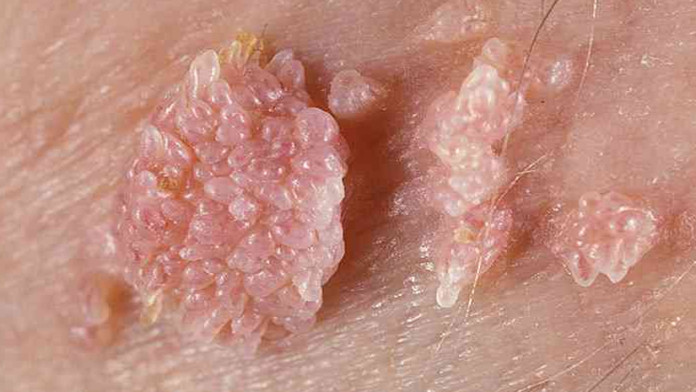
Genital warts – raised, flat, pink, or flesh-colored on anus, cervix, scrotum, groin, thigh, or penis.
 Some types of genital HPV infection are associated with cancer, including cervical cancer and cancer of the vulva, anus, or penis. If infection occurs with one of these virus types, precancerous changes can occur in cells in the tissue without causing any symptoms.
Some types of genital HPV infection are associated with cancer, including cervical cancer and cancer of the vulva, anus, or penis. If infection occurs with one of these virus types, precancerous changes can occur in cells in the tissue without causing any symptoms.
How Is HPV Infection Diagnosed?
The appearance of genital warts is the most common way of diagnosis of HPV infection. Women infected with HPV are told to get a Pap test done and it is the sure fire way to find out the cervical cancer or precancerous changes in the cervix.
 In the HPV test, a doctor takes a swab of cells from the cervix, just as for the Pap test. The cells are then analysed in a laboratory. The test can identify 13 or 14 of the high-risk HPV types associated with cervical cancer. In men, as in women, genital warts reflect HPV infection. But no specific test for the strains of HPV that cause cancer is available at this time for men.
In the HPV test, a doctor takes a swab of cells from the cervix, just as for the Pap test. The cells are then analysed in a laboratory. The test can identify 13 or 14 of the high-risk HPV types associated with cervical cancer. In men, as in women, genital warts reflect HPV infection. But no specific test for the strains of HPV that cause cancer is available at this time for men.
Treatment:
There is no single effective cure for removal of genital warts. A number of treatment options exist; however, no treatment is 100% effective in eliminating warts and preventing them from coming back in all patients. It also is not possible to eliminate infection with human papillomavirus once it has occurred. Genital warts may go away on their own in about 10% to 20% of people over a period of three to four months.
Cryotherapy:
 Laser treatment:
Laser treatment:
 This treatment is used for extensive or recurrent genital warts. It may require local, regional, or general anaesthesia. The laser physically destroys the HPV-induced lesion. It is high cost and scarring
This treatment is used for extensive or recurrent genital warts. It may require local, regional, or general anaesthesia. The laser physically destroys the HPV-induced lesion. It is high cost and scarring
Electrodesiccation:
 This technique uses an electric current to destroy the warts. It can be done in the office with local anaesthesia.
This technique uses an electric current to destroy the warts. It can be done in the office with local anaesthesia.
By: Archa Dave