A strong, multi-“flavoured” layer of adherent bacterial cells lining the surface of our teeth are biofilms. It is the plaque that causes tooth decay and other periodontal diseases. Biofilms form when he bacteria stick to the surfaces in watery environments and secrete slimy substances that can stick to all materials – biological tissues, medical implants, metals, plastics, and soil particles. Biofilms can be formed either by a single bacterial species, or as most commonly seen, a group of bacterial colonies including, algae, fungi, protozoa, debris, and corrosion products.
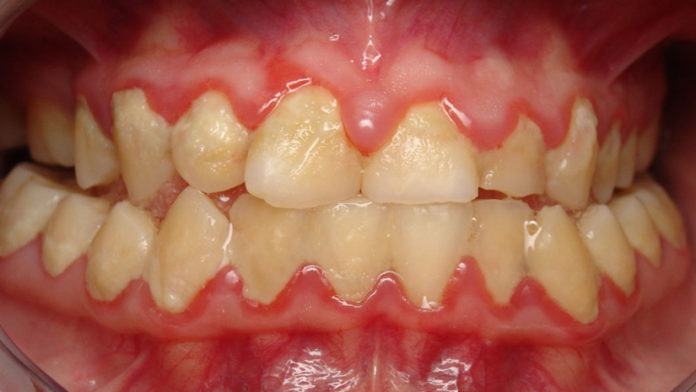
 Dental plaques are the primary cause of dental caries and other major oral infections. Dental plaques exist not only on the tooth but also under the gums, bound closely to one another by an extracellular matrix of polymers.
Dental plaques are the primary cause of dental caries and other major oral infections. Dental plaques exist not only on the tooth but also under the gums, bound closely to one another by an extracellular matrix of polymers.
 Dental plaques are seen on tooth surfaces, smooth surfaces, fissures, and gingival crevices; but most likely they are seen on dental fissures and crevices. The growth process of the plaque biofilm changes from the gram-positive and streptococcus-rich to a gram-negative anaerobe in its more mature state.
Dental plaques are seen on tooth surfaces, smooth surfaces, fissures, and gingival crevices; but most likely they are seen on dental fissures and crevices. The growth process of the plaque biofilm changes from the gram-positive and streptococcus-rich to a gram-negative anaerobe in its more mature state.
Formation of Bio-films:
 Free-swimming bacterial cells arrange themselves in clusters and attach themselves on the surface.
Free-swimming bacterial cells arrange themselves in clusters and attach themselves on the surface.
These cells then begin producing a slushy matrix and signal one another to multiply and form a micro-colony.
These micro-colonies promote the co-existence of diverse bacterial species and metabolic states.
Effects of Bio-films on our health:
 Biofilms are resistant to antibiotics and strong and/or long-term doses are prescribed to eradicate biofilm-related infections. Biofilms are responsible for diseases, such as:
Biofilms are resistant to antibiotics and strong and/or long-term doses are prescribed to eradicate biofilm-related infections. Biofilms are responsible for diseases, such as:
Bacterial endocarditis of the inner surface of the heart and its valves
Cystic fibrosis, resulting in increased susceptibility to serious lung infections
Nosocomial infections, developed from the surfaces of catheters, medical implants, wound dressing, or other medical devices
Legionnaire’s disease, an acute respiratory infection resulting from the aspiration of clumps of Legionella biofilms Otitis media the most common acute ear infection in children
How to control Biofilms on orally used things:
Brushing the teeth and other prostheses to disrupt the biofilm.
Rinse your mouth with an anti-bacterial mouthwash containing a mixture of essential oils in alcohol.
To eliminate unwanted disease causing organisms, ask your dentist to replace your prosthesis every 7 years.
By: Archa Dave